Educational areas
Educational rooms
The campus is equipped with a complex of teaching rooms, most of them centralized in a recent building. Two learning labs and several classrooms are equipped with removable digital equipment for active, dynamic learning:
- writing walls to unleash students' creativity,
- tables and chairs on wheels to facilitate modularity and group work,
- interactive touch screens to encourage a diversity of teaching methods...
A labeling process for the two learning labs is underway as part of the national Learning Lab Network foundation, in order to enhance the value of these spaces and develop innovative teaching practices.
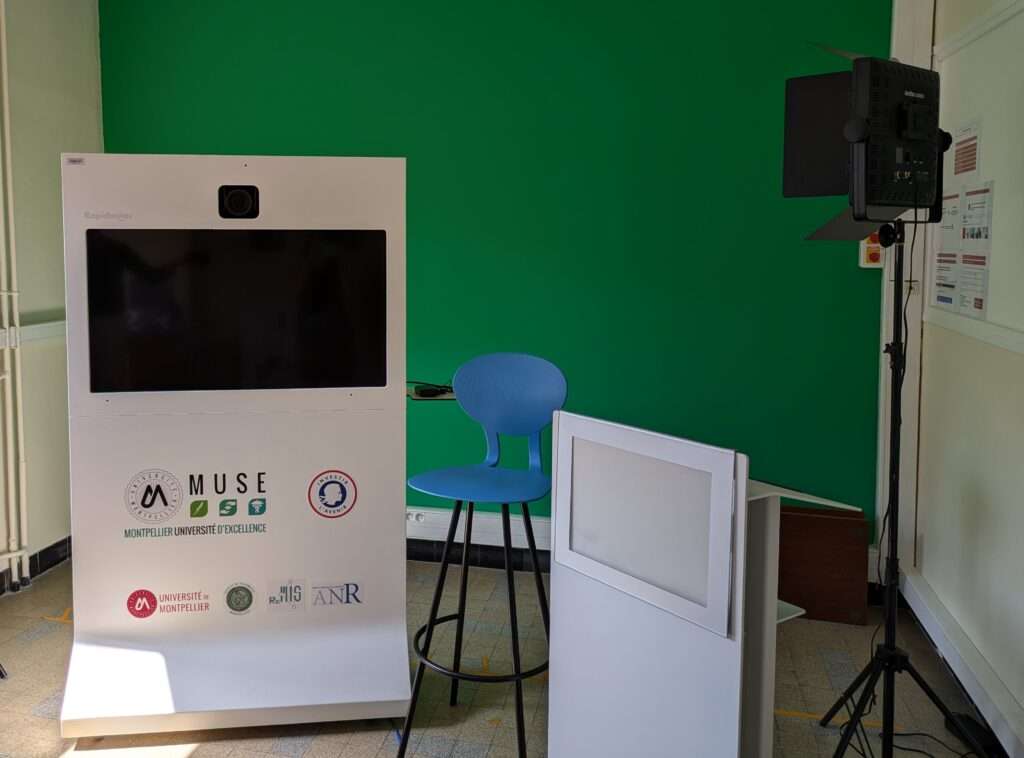
RapidMooc
The RapidMooc, or mini recording studio, enables teachers and accompanied students to record professional-quality video clips. These capsules are produced as part of teaching projects set up with the campus educational engineer, e-learning courses or for communication media.

3d printing platform
As part of the IDEFI REMIS program, the Health Engineering program at the University of Montpellier has created a 3D printing platform for its Health Engineering and Pharmacy Bachelors and Masters students: EPI3DS (Espace pédagogique d'impression 3D pour la Santé). The aim is to introduce students to various 3D printing techniques and computer-aided design.

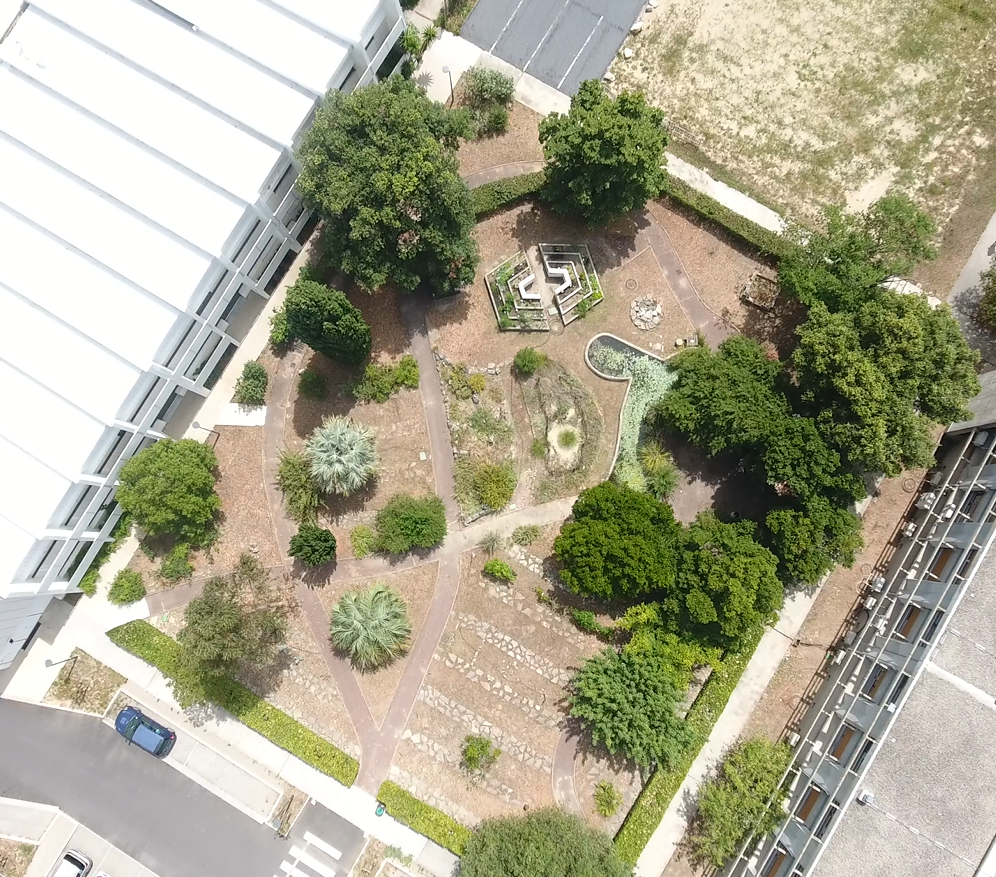
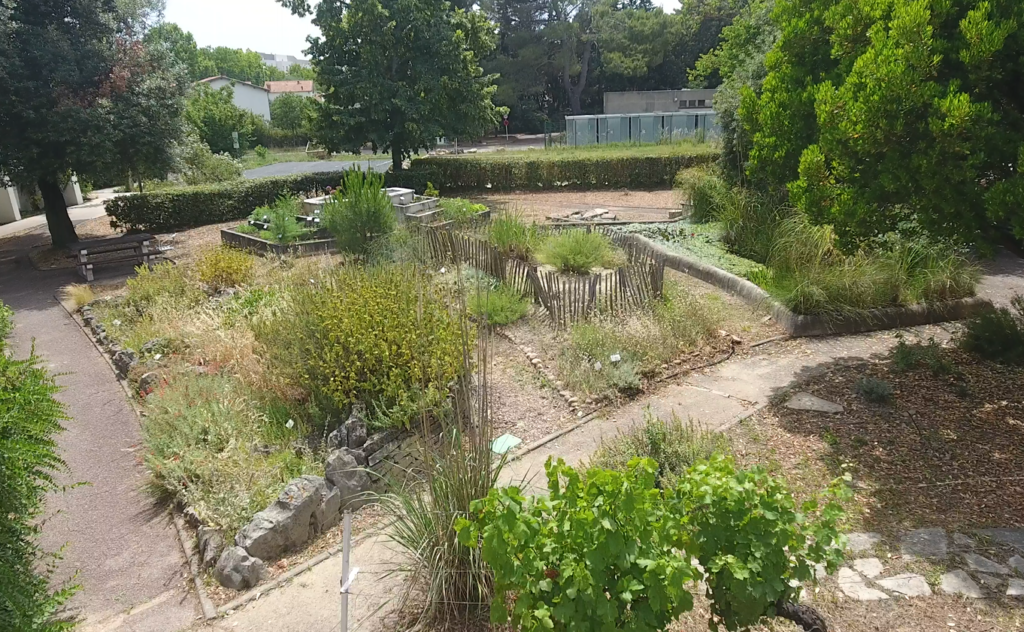
The connected botanical garden
As part of the refurbishment of our Faculty's botanical garden, the entire pedagogical team of the Botany, Phytochemistry and Mycology Laboratory has been mobilized to bring this place of enjoyment, but above all of plant study for pharmacy students, into the 21st century.
In addition to the installation of a new watering system and new plants for teaching purposes, a list of the valid Latin names of the plants has been drawn up, together with their French names and families. Each specimen is identified by a small data sheet, including a QR code linking to summary sheets. By scanning the code with a cell phone, you can access additional photos of the plant and botanical information at any time of year. The medicinal use of the plant is also described.
This pedagogical innovation will benefit students and enable them to better understand their botany courses. As well as benefiting students through e-learning, these new labels will also be of interest to members of our faculty who often lunch in the gardens on our campus, and even to the general public with an interest in plants.
How do virtual cards work?
To access the virtual plant sheets, you need a QR code-reading application on your smartphone (ScanLife, for example). Once you've scanned the QR code close enough to the plant label (as if you were taking a photo), you can download a description of the plant in question onto your phone. There are several data sources (Tela Botanica, SmartJardin and internal database) and therefore different file formats. Below, the one for the olive tree (source: SmartJardin).

The garden in photos :





